Description
However it can be used in combination with amoxicillin trihydrate (under the trade name Augmentin) for treatment of a variety of bacterial infections, where it prevents antibiotic inactivation by microbial lactamases. It has a role as an antibacterial drug, an EC 3.5.2.6 (beta-lactamase) inhibitor and an antimicrobial agent. It contains a clavulanate.
|
Molecular Formula |
C8H8KNO5 |
|
Synonyms |
Potassium clavulanate 61177-45-5 CLAVULANATE POTASSIUM Amonate |
Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
- Silicon dioxide Usage And Synthesis
|
General Description |
Silicon dioxide occurs almost everywhere on earth. It is one of the most important and abundant oxides on earth, constituting about 60% weight of the earth’s crust as silica itself or in combination with other metal oxides in silicates. It commonly is found as sand in the vast ocean and river shores, their beds, deserts, rocks, and minerals. |
|
Uses |
|
|
Chemical Properties |
Diatomaceous earth is a transparent to gray, odorless amorphous powder. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Amorphous silica, the nanocrystalline form of SiO2, is a transparent to gray, odorless, amorphous powder |
|
Chemical Properties |
white crystals or powder |
|
Uses |
Functionalized RAFT agent for controlled radical polymerization; especially suited for the polymerization of styrene; acrylate and acrylamide monomers. Azide group can be used to conjugate to a variety of alkyne-functionalized biomolecules. Chain Transfer Agent (CTA). |
|
Uses |
SDS mixture of sodium alkyl sulfates consisting chiefly of sodium lauryl sulfate |
|
Uses |
manufacture of glass, water glass, refractories, abrasives, ceramics, enamels; decolorizing and purifying oils, petroleum products, etc.; in scouring- and grinding-compounds, ferrosilicon, molds for castings; as anticaking and defoaming agent. |
|
Uses |
Silica (SiO2) (RI: 1.48) is mined from deposits of diatomaceous soft chalk-like rock (keiselghur). This is an important group of extender pigments, which is used in a variety of particle sizes. They are used as a flatting agent to reduce gloss of clear coatings and to impart shear thinning flow properties to coatings. They are relatively expensive. |
|
Uses |
silica is also known as silicone dioxide. Silica has a variety of applications: to control a product’s viscosity, add bulk, and reduce a formulation’s transparency. It can also function as an abrasive. In addition, it can act as a carrier for emollients, and may be used to improve a formulation’s skin feel. Spherical silica is porous and highly absorbent, with absorption capabilities roughly 1.5 times its weight. A typical claim associated with silica is oil control. It is found in sunscreens, scrubs, and wide range of other skin care, makeup, and hair care preparations. It has been successfully used in hypoallergenic and allergy-tested formulations. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A silicon oxide made up of linear triatomic molecules in which a silicon atom is covalently bonded to two oxygens. |
|
Hazard |
Not toxic if ingested, inhaled silica dust can cause silicosis; carcinogen. |
|
Agricultural Uses |
Silica is silicon dioxide, one of the most abundant materials on the earth’s crust. Quartz is an example of silica. It is used as a filler in fertilizers, and also, in the manufacture of glass, ceramics, abrasives, rubber and cosmetics. |
|
Safety Profile |
The pure unaltered form is considered a nuisance dust. Some deposits contain small amounts of crystahne quartz and are therefore fibrogenic. When diatomaceous earth is calcined (with or without fluxing agents) some sdica is converted to cristobalite and is therefore fibrogenic. Tridymite has never been detected in calcined batomaceous earth. See also other silica entries |
|
Potential Exposure |
Diatomaceous earth is used as a filtering agent and as a filler in construction materials, pesticides, paints, and varnishes. The calcined version (which has been heat treated) is the most dangerous and contains crystallized silica, and should be handled as silica. See also other entries on silica |
|
Shipping |
This material is not singled out by DOT in its Performance-Oriented Packaging Standards. |
|
Purification Methods |
Purification of silica for high technology applications uses isopiestic vapour distillation from concentrated volatile acids and is absorbed in high purity water. The impurities remain behind. Preliminary cleaning to remove surface contaminants uses dip etching in HF or a mixture of HCl, H2O2 and deionised water [Phelan & Powell Analyst 109 1299 1984]. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Silica, amorphous is a noncombustible solid. Generally unreactive chemically. Incompatible with fluorine, oxygen difluoride, chlorine trifluoride. Soluble in molten alkalis and reacts with most metallic oxides at high temperature. |
|
Waste Disposal |
Sanitary landfill. |
Additional information
Safety
|
Signal |
Danger |
|
GHS Hazard Statements |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 57 companies from 9 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. H228 (100%): Flammable solid [Danger Flammable solids] H252 (75.44%): Self-heating in large quantities; may catch fire [Warning Self-heating substances and mixtures] H317 (70.18%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin] H319 (22.81%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H334 (70.18%): May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled [Danger Sensitization, respiratory] H361 (14.04%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |




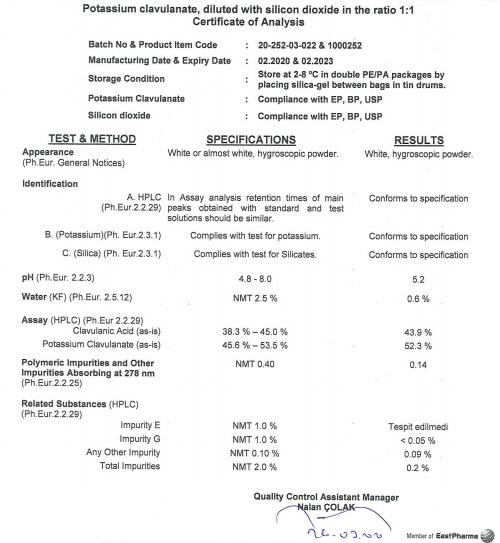

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.