Description
Other cases of the application of Bitumen are preserving materials, dead bodies’ mummification, fixing bricks, keeping water, etc.
Man has been informed about ASPHALT materials for a long time and it has been used in different parts of the world in different fields. Using PURE BITUMEN in modern industries started after PETROLEUM was discovered and reached its peak in the 2nd half of the 20th century.
TYPES OF BITUMEN REGARDING THE GENERATION SOURCE
Regarding its generation source Bitumen can be classified into three categories:
1. NATURAL BITUMEN
NATURAL BITUMEN or NATIVE ASPHALTS are a class of BITUMENs which have been naturally produced due to climate conditions in the course of time, and are used without the need to be processed in distillation ways; they are very varied regarding their composition and properties.
2. PETROLEUM ASPHALT
Petroleum ASPHALT are the Bitumen’s which are derived from petroleum. These are solid and semi solid Bitumen’s which are directly produced through distillation from petroleum or by additional operations such as air blowing. Compared with the other types, they are more commonly used and have more applications.
3. COAL TAR PITCHES
Coal tar Pitches are hard black substances which are formed as the result of coal tar distillation. Their new broken surface is shiny and when they are heated they, along with fast decrease in viscosity, melt and their melting point depends on the production process.
TYPES OF BITUMEN REGARDING THEIR APPLICATION
Regarding their applications, Bitumen’s can be divided into two groups: road
construction or thin Bitumen, and building Bitumen and (roof insulator) or hard
Bitumen. About 90% of the produced Bitumen is used in road construction activities and 10% of it is used for insulation applications. In Iran, the main part of Bitumen is used in the road construction activities and by the municipalities for coating the streets. Road construction Bitumen is usually classified according to its penetration.
The penetration rate of Bitumen material represents its strength and hardness which is defined as the number of penetration unit (one tenth millimeter) of one vertical standard needle in one Bitumen sample, in certain time and weight on the needle and temperature. The penetration rate of Bitumen is usually measured 25 degree centigrade with 100 gram weight and in 5 seconds. Road construction Bitumen’s made in Iran are “60 to 70” and ’85 to 100”.
The numbers represent the range of Bitumen penetration rate. Bitumen is hydrocarbon substance which is black to dark brown and quite solvable in carbon sulfur. It is solid in normal environment temperature but in increased temperature it first becomes paste and then liquid. It has two important properties, impenetrable against water and adhesiveness which makes it an important material for application.
KINDS OF BITUMEN FROM VIEW POINT OF ITS STRUCTURE
Bitumen is usually acquired from petroleum distillation. Such kind of Bitumen is called petroleum asphalt or distillery Bitumen. Petroleum Bitumen is the product of two stages of petroleum distillation in distillation tower. In the first stage of distillation, light materials such as gasoline and propane are separated from raw oil. This process is done in the pressure close to atmosphere pressure. In second stage heavy compounds such as diesel oil and kerosene are extracted. This process is done in a pressure close to vacuum pressure. Finally a mixture of solid bits called Asphaltine is remained which is floated in a grease-like fluid, called malton. Some kinds of Bitumen is acquired from nature by gradual changing of petroleum and the evaporation of its evaporating materials by passing a many years, such kind of Bitumen is called natural Bitumen, and it is more lasting than petroleum asphalts.
Such Bitumen may be found in nature in pure form (lake Bitumen) or extracted from mines (Mineral Bitumen).

1) BLOWN BITUMEN
Blown Bitumen comes from hot air blown to pure Bitumen in the last stage of
refining. In this process, hot air having 200-300 degree centigrade temperature is blown to Bitumen container with porous tubes. In this process, hydrogen atoms in Bitumen hydrocarbon are combines with oxygen in the air and by forming water, polymerization happens. Compared with pure Bitumen, BLOWN BITUMEN or OXIDIZED BITUMEN has a low penetration rate and a high softness point. This kind of Bitumen is used in making roof sheets, automobile battery and coating.
2) MIXED OR SOLUTION BITUMEN
Mixed Bitumen is a term used to refer to a mixture of Bitumen and a suitable liquid (for example kerosene or gasoline). This Bitumen in normal environment
temperature is liquid, or is changed to liquid with a little heat. Mixed Bitumen is used in different kinds of macadam and COATING ASPHALTS. The speed of its clotting or hardening depends on the kind of liquid. For example because of high speed of gasoline evaporation, Bitumen solved in gasoline hardens faster.
This Bitumen is called rapid clotting (RC) Bitumen. The Bitumen solved in kerosene is called mild clotting (MC) Bitumen and those solved in gas oil or fuel oil is called slow clotting (SC). Liquid Bitumen is classified according to their viscosity rate.
3) EMULSION BITUMEN
Emulsion Bitumen is produced by mixing Bitumen, water, and an emulsion making material. The emulsion making material is usually alkali salt of an organic acid or ammonium salt which charges Bitumen particles. So the Bitumen particles expel each other because of their induction charges and float in the form of balls having one hundredth to one thousandth millimeter diameter. The use of such kind of Bitumen decreases environment pollution and as oil or flammable solvents aren’t used the danger of flaming during transportation is decreased.
BITUMEN SPECIFICATIONS AND CHARACTERISTICS
In order to specify the components of Bitumen different methods are used and in most of these methods Bitumen solved in sulfur carbon is divided in three major parts:
• Carbon: the part which is insoluble in tetra chloride carbon
• Asphaltine: insoluble part in solvents such as light aliphatic hydrocarbons such as ether
• Malton: solved part in light aliphatic hydrocarbons such as heptane. Maltons are divided into two minor groups, resins and oils, and while resin materials are brown and semi hard, they provide Bitumen flexibility and adhesiveness. Heavy oils make Bitumen soft, the more its amount the softer Bitumen will be.
The kind and the percentage of the mentioned materials depend completely on the oil or mineral basis of the Bitumen and the percentage of these materials can be changed with the help of their oxidation process.
GENERAL CLASSIFICATION OF BITUMEN IS PRESENTED IN THE FOLLOWING TABLE:
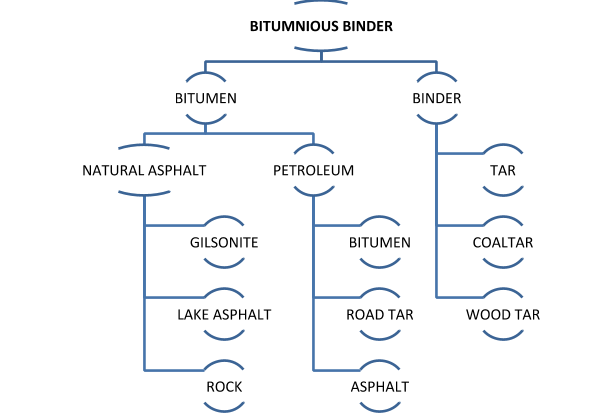
Petroleum bitumen is known by different names throughout the world. For example, the term “BITUMEN” is used as synonymous with the term “ASPHALT”, or “ASPHALT BINDER” used in North America. In lots of countries, the term “ASPHALT” is used to describe mixtures of bitumen with mineral materials. Coal derived products such as coal tar or coal-tar pitches are very different from bitumen.
These are manufactured by the high-temperature pyrolysis (>800°C) of bituminous
coals and differ from bitumen substantially in composition, physical characteristics, and potential health risks. Petroleum pitches, which are often highly aromatic residuums, produced by thermal cracking, coking or oxidation from selected petroleum fractions are also significantly different from bitumen. Bitumen also should not be confused with natural or lake asphalt such as Trinidad Lake Asphalt, Gilsonite, rock asphalt and Selenice that are sometimes used as additives in end use applications. These products are unrefined and not produced by refining of crude oils. They often contain a high proportion of mineral matter (up to 37% by weight) and light components, leading to a higher loss of mass when heated. In the world more than seven kinds of BITUMEN are produced which depends on climate and region conditions, but in Iran BITUMEN production is limited to two kinds due to high expenses. At present BITUMEN 85/ 100 with high penetration and BITUMEN 60 /70 with less penetration is produced. According to this classification in
cold places BITUMEN 85/100 and in warm places BITUMEN 60/70 BITUMEN are used.
The BITUMEN flexibility makes asphalts lose their resistance in cold and hot
climates. In desert regions, cold nights make asphalt contract and the warmth of its days separates its components and the asphalt breaks.
In many countries in order to increase the BITUMEN flexibility, polymer is added to it.
In this way they increase the flexibility of the BITUMEN. The production of multi grit BITUMEN in developed countries isn’t an extraordinary or hard affair. They know that for five year BITUMEN shouldn’t be repaired or dug, and they increase the life of asphalt to 20 years in this way, and never ignore its repair and maintenance.
Besides BITUMEN type, roadbed and preparation of asphalt bed is also important. In making asphalt, 4 to 5 percent BITUMEN and 96 percent other materials are used; many of the faults lie on drainage, improper roadbed, neglecting region traffic volume and uncoordinated fulfillment of the project. The method of fulfillment in asphalt section is not according to established principles, and in order to gain more benefit most of the norms are disregarded.
GENERAL INFORMATION OF BITUMEN:
BITUMEN is the heaviest section of petroleum and one of the most complicated parts of it which can be seen in dark color and in the solid, semi solid or viscose states, whether natural or synthetic. The main components of BITUMEN are hydrocarbon compounds having high molecular masses which consist of oil, resin and asphaltine substances. This substance has a very complicated chemical composition, and among its physical characteristics are viscosity, and being damp proof; it is solvable in carbon disulphide and CO2.
In some countries the term asphalt is used as the equivalent of BITUMEN, but in Iran asphalt is commonly known as a mixture of BITUMEN and sand which is used in road construction process.
BITUMEN is a very dense and black material which is nearly in solid state in normal conditions. It has a complicated chemical structure, and the researches made so far have not been able to offer a definite theory regarding its chemical structure. The reason is that petroleum from which BITUMEN is generated is formed in various geophysical conditions thus it has many different forms. By definition “BITUMEN is a substance which can be solved in carbon sulfur. However, the BITUMEN used in road construction contains less than 0.1 % of materials which are insolvable in carbon sulfur. Though this material, known as carboide , has a slight impact in the BITUMEN impurity , if exposed to high heat its molecules will be broken and this has
been realized as a damage to road asphalt.
Bitumen Grade offered by us
• BITUMEN 20/30
• BITUMEN 35/50
• BITUMEN 40/50
• BITUMEN 40/60
• BITUMEN 50/70
• BITUMEN 60/70
• BITUMEN 70/100
• BITUMEN 80/100
• BITUMEN 85/100
• BITUMEN 100/150
• BITUMEN 160/220
PRODUCING OXIDZED BITUMEN (BLOWN ASPHALT) 99.5% Pure and without using any Gilsonite and other impurities in Refinery by below grades:
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 10/20
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 85/25
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 85/40
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 90/10
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 90/15
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 90/40
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 95/25
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 110/30
• OXIDIZED BITUMEN 115/15
OXIDIZED BITUMEN or BLOWN BITUMEN are produced by passing air through the penetration grades.
- Oxidized bitumen has a wide variety of Industrial applications:
- Foundation damp-proofing
- As bonding Bitumen for roofing sheets memberance Roll and pour application of bitumen
felts.
Sealing of laps and joints of various bituminous felts and membranes. - As a hot applied waterproofing layer
- Foundation damp proofing
- Carpet tile manufacturer
- As a raw material for liquid Bitumen, coating
- For the production of bituminous paint, mastic
- For rust proof pipe coating
- Used as an anti-slip layer compound in the pilling Industry
- Road resurfacing and repair
- Used for production of roofing and sound dampening felts
- Roll and pour application of bitumen felts
- Oxidized Bitumen high softening temperatures quality them as the excellent sealant for
- prevention from bleeding in high temperature applications
Company has various kind of packing in Refinery for produced BITUMEN & OXIDIZED BITUMEN
(SOLID BITUMEN) like Drum, Poly Bags, Carton Box, Polyamide Bag, Kraft Bag and Blocks as below:
DRUM PACKING:
– New steel Drums 185Kg
– New Steel Drums 150Kg
• POLY BAG PACKING:
– Poly Bags 300 Kg
– Poly Bags 500 Kg
– Poly Bags 1000 Kg (1 MT)
OXIDIZED BITUMEN (HARD BITUMEN) PACKING TYPE: CATON BOX:
– Carton Box 20Kg
– Carton Box 25Kg
– Carton Box 40Kg
OXIDIZED BITUMEN Carton boxes have insider nonstick layer that remove easily on BITUMEN. •
MELTABLE POLYAMIDE BAGS:
– Polyamide Bags 20Kg
– Polyamide Bags 25 Kg
Produced BLOWN BITUMEN in Meltable Polyamide bags have extra cover Bags to protect main bags in transportation process.
– KRAFT BAGS :
– Kraft Bags 20Kg
– Kraft Bags 25Kg
– Kraft Bags 40Kg
Produced OXIDIZED BITUMEN in Kraft Bags have extra cover Bags to protect main bags in transportation process.
OXIDIZED BITUMEN IN Block PACKING:
– Blocks 20Kg
– Blocks 25Kg
– Blocks 40Kg
OXIDIZED BITUMEN Blocks have extra cover to protect main block.
STEEL DRUMS:
– Drums 20Kg
– Drums 25Kg
Suitable for direct heating of OXIDIZED BITUMEN.
Other size of packing for OXIDIZED BITUMEN (BLOWN ASPHALT) by Customer request is welcome.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.